How Sleep Deprivation Destroys Your Immune System is a critical topic that reveals the profound impact of insufficient sleep on our body’s defenses. Sleep is not merely a time for rest; it’s an essential phase during which our body rejuvenates and fortifies itself. In understanding the connection between sleep and immunity, we uncover vital insights into how our daily habits affect our health and well-being.
As we explore the physiological effects of sleep deprivation, we’ll learn about the crucial stages of sleep and their significance in maintaining robust health. Not only does sleep deprivation affect mental clarity and physical performance, but it also has far-reaching effects on our immune system, which plays a pivotal role in protecting us against illnesses and infections.
Understanding Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation is not just a matter of feeling tired; it can have serious physiological effects on the body and mind. When we don’t get enough sleep, it can disrupt various bodily functions, leading to a cascade of negative health outcomes. The importance of sleep cannot be overstated, as it serves essential roles in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Physiologically, sleep deprivation affects the body in several key ways. It alters hormone levels, including those that regulate stress and appetite, leading to increased levels of cortisol and decreased levels of leptin, which may contribute to weight gain and increased stress. Furthermore, sleep deprivation negatively impacts the immune system by reducing the production of cytokines, proteins that are crucial for fighting infections and inflammation. Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can increase susceptibility to illnesses, making recovery significantly more challenging.
Stages of Sleep and Their Importance
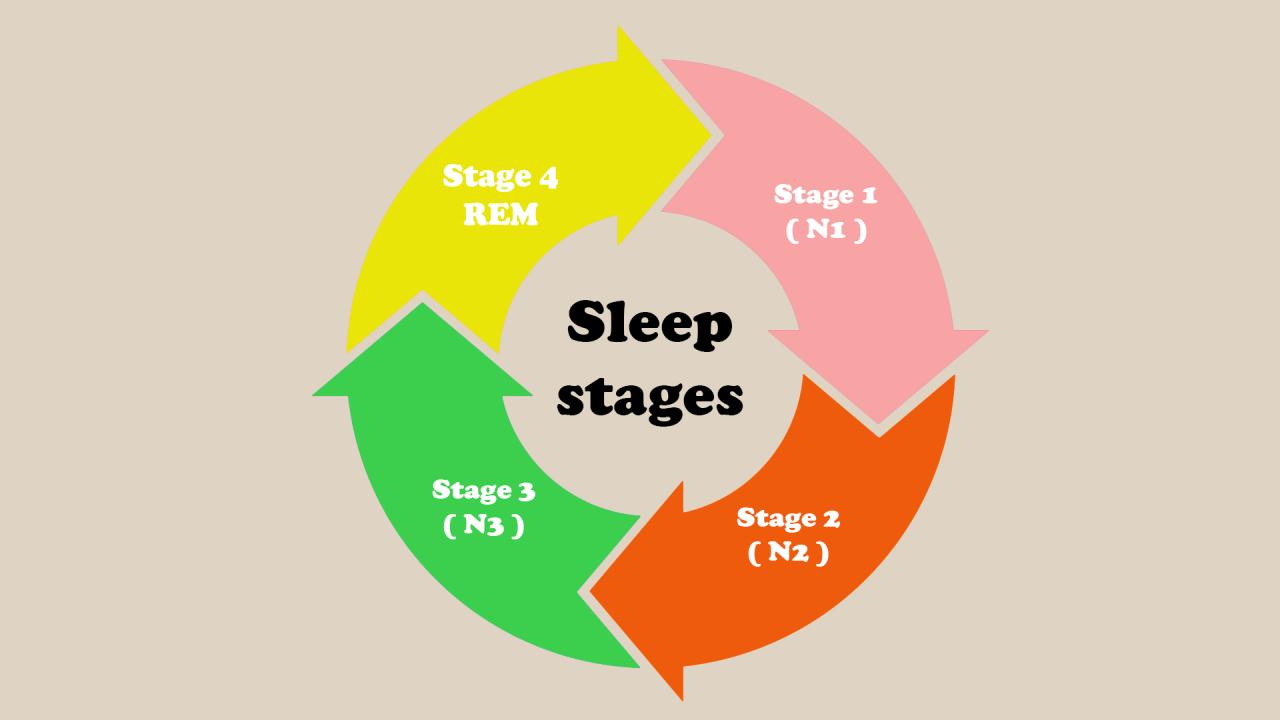
Understanding the different stages of sleep is critical for appreciating how lack of sleep impacts health. Sleep is divided into two primary types: non-REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and REM sleep, each comprising distinct stages that play unique roles in bodily functions.
During non-REM sleep, the body cycles through three stages:
1. Stage 1: Light sleep, where you drift in and out of sleep and can be easily awakened.
2. Stage 2: Onset of true sleep, where heart rate slows, and body temperature drops. This stage is crucial for memory consolidation.
3. Stage 3: Deep sleep, essential for physical recovery and growth, as well as immune function restoration.
REM sleep, which occurs after about 90 minutes of sleep, is where most dreaming occurs. This stage is important for emotional regulation and memory processing.
Inadequate sleep disrupts these stages, leading to insufficient time spent in deep sleep and REM sleep. Without these restorative processes, individuals often experience diminished cognitive performance, including impaired attention, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities.
Impact on Mental and Physical Performance
The consequences of sleep deprivation extend into both mental and physical performance, leading to a range of detrimental effects.
Mental performance suffers as sleep-deprived individuals typically experience:
– Impaired Concentration: Difficulty focusing on tasks, leading to decreased productivity.
– Memory Issues: Reduced ability to recall information and learn new skills.
– Mood Disturbances: Increased irritability, anxiety, and depression, often exacerbated by prolonged lack of sleep.
Physically, the ramifications are equally concerning. Lack of sleep can lead to:
– Decreased Coordination: Slower reaction times and increased risk of accidents.
– Altered Metabolism: Disruption in metabolic processes, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity.
– Increased Risk of Chronic Conditions: Higher susceptibility to conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
In summary, sleep deprivation has far-reaching effects on both mental and physical health, emphasizing the need for adequate sleep to maintain a functional and healthy life.
The Immune System Explained
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Understanding its components and functions is crucial for recognizing how sleep deprivation can impact our health.
The immune system comprises various components that play pivotal roles in identifying and neutralizing threats. Major players include white blood cells (leukocytes), antibodies, the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. Each component has specific functions. For instance, white blood cells are the primary defenders; they can be categorized into several types, including lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) and phagocytes, which engulf and destroy invaders.
Response to Pathogens and Infections
When the immune system detects a pathogen, it initiates a response that involves a series of coordinated actions. This response can be described in several key stages:
1. Recognition: The immune system identifies foreign invaders through specific markers called antigens.
2. Activation: Once recognized, immune cells are activated. T cells help orchestrate the response, while B cells produce antibodies that specifically target the invaders.
3. Elimination: Activated immune cells work to eliminate the pathogens through various mechanisms, including direct destruction and the release of signaling molecules that recruit additional immune components.
4. Memory: After an infection, the immune system retains a memory of the pathogen through memory cells. This enables a quicker and more efficient response if the same pathogen invades again.
The efficiency of this response is critical in maintaining overall health, highlighting the importance of a well-functioning immune system.
Relationship Between Sleep and Immune System Efficiency
Sleep plays a vital role in the overall efficiency of the immune system. When we sleep, the body undergoes several restorative processes that enhance immune function. Lack of sleep can lead to impaired immune responses, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Several key points illustrate this relationship:
– Cytokine Production: Sleep deprivation reduces the production of cytokines, which are essential for mediating the immune response during infection and inflammation.
– Reduced Antibody Response: Inadequate sleep can weaken the antibody response, diminishing the effectiveness of vaccines and the body’s ability to fend off infections.
– Increased Inflammation: Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with heightened levels of inflammatory markers in the body, indicating an overstimulated immune response without effective regulation.
The importance of sleep for a robust immune response cannot be overstated; sufficient rest is essential for optimal health and resilience against diseases.
Understanding these components and their interconnectedness reveals how sleep deprivation can undermine the immune system’s ability to protect the body effectively. By prioritizing sleep, individuals can enhance their immune function and overall health.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Immunity: How Sleep Deprivation Destroys Your Immune System

Sleep deprivation can have profound effects on the immune system, leading to a range of health issues. Research in this area has revealed a direct correlation between lack of sleep and weakened immune responses. Studies have shown that sleep is not merely a passive state but a critical period for immune function optimization and restoration.
Studies Demonstrating Impact on Immune Response
Numerous studies have demonstrated how sleep deprivation affects various aspects of immune function. One pivotal study conducted by Prather et al. in 2015 observed that individuals who experienced less than seven hours of sleep were nearly three times more likely to catch a cold compared to those who slept eight hours or more. This highlights the direct relationship between sleep duration and susceptibility to infections.
Another significant study published in the journal *Sleep* found that immune markers, such as cytokines, were adversely affected by restricted sleep. Participants who were sleep-deprived showed lower levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, both critical for the immune response. This underscores the importance of adequate sleep for maintaining robust immune defenses.
Mechanisms by Which Sleep Deprivation Weakens Immune Functions
The mechanisms underlying the impact of sleep deprivation on immunity are multifaceted. Sleep plays a crucial role in the production of cytokines, proteins that are vital in the immune response. When sleep is compromised, the body’s ability to produce these cytokines diminishes, leading to a weakened immune reaction.
Additionally, sleep deprivation leads to increased levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, which can further suppress immune function. Chronic elevation of cortisol can inhibit the proliferation of lymphocytes, which are essential for adaptive immunity. This disruption can leave individuals more vulnerable to infections and illnesses.
Increased Illness Incidence in Sleep-Deprived Individuals, How Sleep Deprivation Destroys Your Immune System
Statistics surrounding sleep deprivation and illness incidence reveal alarming trends. According to the National Sleep Foundation, adults who sleep less than six hours a night are at a significantly higher risk for various health issues, including chronic illnesses. This statistic is particularly concerning as it correlates with a rise in flu and cold infections among this demographic.
Research indicates that sleep deprivation can increase the risk of developing conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases, further illustrating the far-reaching impact of inadequate sleep. The immune system’s compromised state not only heightens susceptibility to infections but also can lead to longer recovery times and increased severity of illnesses.
“Sleep deprivation is a major factor contributing to impaired immune responses, increasing the likelihood of illness.”
Strategies for Improving Sleep Quality
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining a robust immune system and overall well-being. Many people struggle with sleep deprivation, which can lead to various health issues. Fortunately, there are effective strategies to enhance sleep hygiene and ensure a restful night. By implementing these methods, individuals can improve their sleep quality and, consequently, their immune function.
Effective Methods to Enhance Sleep Hygiene
Maintaining good sleep hygiene is crucial for improving sleep quality. Here are some effective methods to consider:
- Establish a Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, cool, and quiet. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.
- Avoid Stimulants: Limit caffeine and nicotine intake, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep.
- Limit Screen Time: Reduce exposure to screens from phones, computers, and TVs at least one hour before bed, as blue light can interfere with melatonin production.
- Be Mindful of Food and Drink: Avoid heavy meals and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep.
Guide for Establishing a Consistent Sleep Routine
Creating a consistent sleep routine can significantly enhance sleep quality. A structured plan helps signal the body when it’s time to wind down. Here’s a simple guide:
1. Wind Down: Begin a pre-sleep routine 30-60 minutes before bed. Engage in relaxing activities such as reading or taking a warm bath.
2. Wind Down Rituals: Incorporate calming rituals such as gentle stretching or practicing deep breathing exercises to ease tension and prepare for sleep.
3. Consistent Wake-Up Time: Set your alarm for the same time each morning to promote a regular sleep schedule. This consistency helps regulate your body’s sleep-wake cycle.
4. Limit Naps: If necessary, keep daytime naps to 20-30 minutes and avoid napping late in the afternoon to ensure nighttime sleep is not disturbed.
5. Adjust Gradually: If needing to shift your sleep schedule, adjust by 15-30 minutes each night until the desired bedtime is achieved.
Relaxation Techniques to Improve Sleep Quality
Incorporating relaxation techniques into your nightly routine can significantly enhance sleep quality. Here are some methods to consider:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Focus on slow, deep breaths to calm the mind and body. Inhale deeply through the nose for a count of four, hold for four, and exhale slowly for a count of six.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and relax different muscle groups, starting from your toes and working up to your head. This practice helps release physical tension.
- Meditation or Mindfulness: Engage in guided meditation or mindfulness practices to clear your mind and promote relaxation before sleep.
- Aromatherapy: Use calming scents like lavender or chamomile through essential oils or candles to create a soothing atmosphere conducive to sleep.
- Gentle Yoga: Practice gentle yoga stretches to relax the body and release tension, especially in the evening.
Implementing these strategies can lead to significant improvements in sleep quality, ultimately contributing to better immune function and overall health.
Final Summary
In summary, the effects of sleep deprivation extend beyond mere tiredness; they significantly compromise our immune system’s ability to function effectively. By recognizing the vital link between quality sleep and immune health, we can better appreciate the importance of good sleep hygiene and adopt practical strategies to improve our sleep. Prioritizing rest is not just about feeling good—it’s essential for maintaining our overall health and resilience against disease.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the signs of sleep deprivation?
Common signs include fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and weakened immune response.
How many hours of sleep do adults need?
Most adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night for optimal health.
Can napping help reduce the effects of sleep deprivation?
Short naps can help alleviate some effects of sleep deprivation, but they cannot replace a full night’s sleep.
Is sleep deprivation linked to chronic illnesses?
Yes, chronic sleep deprivation is associated with various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
What lifestyle changes can improve sleep quality?
Establishing a regular sleep schedule, minimizing screen time before bed, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can enhance sleep quality.